What Is Schema?

A Beginner’s Guide to Structured Data and How It Works
Schema is one of the most important — yet often overlooked — elements in modern SEO. Short for “Schema markup,” this structured data language helps search engines understand the content of your webpages more clearly. Whether you're running a blog, a business site, or an e-commerce store, understanding what schema is — and how it works — can significantly improve how your pages appear in search results.
In the simplest terms, schema is a form of structured data — a standardized way to label and organize information on your site so that search engines like Google can read, interpret, and display it more effectively. Instead of just crawling your site for raw text, search engines use schema markup to identify key components such as product names, reviews, events, articles, and frequently asked questions. This enhanced understanding allows search engines to produce rich snippets, knowledge panels, and other advanced visual elements in search results, all of which can boost click-through rates and user trust.
Structured data SEO relies heavily on schema because it provides the clarity needed to signal intent and content type. When properly implemented, schema in SEO acts as a translator between your content and the algorithms that determine ranking and relevance. From blog posts to service pages, adding schema markup creates a more intelligent, search-friendly experience.
This beginner-focused guide will walk you through the core principles of schema, the different types of markup available, and how structured data and SEO work together to elevate your visibility in competitive search landscapes. Whether you're just starting or looking to enhance your site's foundation, understanding the role of schema markup is your first step toward smarter optimization.
What Makes Schema Different from Other On-Page SEO Elements

When optimizing a website for SEO, most people focus on elements like page titles, meta descriptions, header tags, and internal links. While these components are crucial, they primarily help users and search engines interpret visible content. Schema, on the other hand, works beneath the surface. It adds a structured layer of information that isn't designed for human readers — it's designed specifically for machines, using a shared vocabulary from Schema.org.
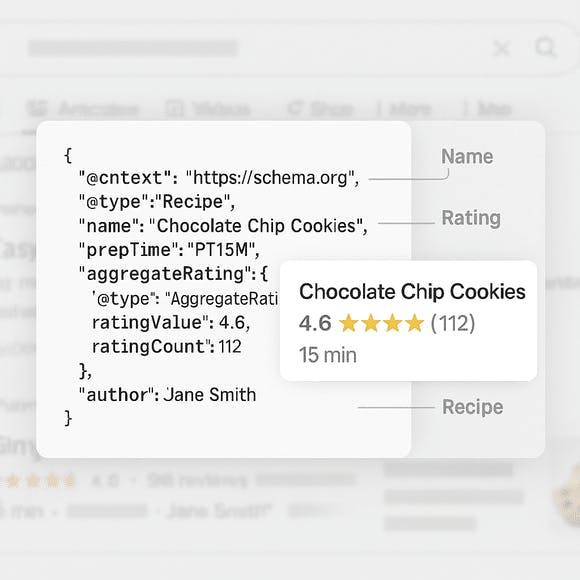
Unlike traditional on-page elements that enhance readability and structure, schema markup gives explicit context about your content. For example, a page title might say “Blueberry Muffin Recipe,” but schema can define that page as a Recipe, highlight preparation time, ingredients, calories, user ratings, and even dietary information — all in a structured data format like JSON-LD. This added context increases the likelihood of rich results in search, such as recipe cards, FAQs, product listings, or event previews.
Another key distinction is that schema isn't just about labeling content — it's about describing relationships and intent. Schema.org vocabulary allows you to identify entities and define how they interact. You can mark a person as the author of an article, a review as feedback on a product, or an event as being hosted by a specific organization. These connections help search engines build more complete knowledge graphs, which they use to return better, more contextualized results to users.
It’s also important to note that schema markup doesn't change how your content looks to users — it’s embedded in the code, silently enhancing how search engines interpret your pages. Structured data and SEO work together, but schema represents a layer of optimization that directly impacts how your pages are featured. When implemented properly, it complements — not replaces — core SEO strategies like keyword targeting, content hierarchy, and meta optimization.
In short, schema provides a level of semantic clarity that traditional tags cannot. It turns flat, human-readable content into structured, machine-readable data that fuels enhanced listings, stronger relevance signals, and better user engagement through rich results.
How Schema Works Behind the Scenes

Schema markup works by embedding structured data into your website's HTML, using a specific format that search engines can easily parse. The most commonly recommended format is JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data), which allows the data to exist independently of the visible page content. This means search engines can extract and process the information without interfering with how users view the site, making it ideal for structured data SEO.
When a search engine bot crawls your webpage, it doesn’t just read the words on the screen — it also looks for structured cues that indicate meaning. Schema markup acts like a set of labels that clearly define what each piece of content is. For example, it can specify that a certain string of text is a product name, that a number represents a rating, or that a date refers to an event start time. This clarity allows search engines to interpret content more accurately, increasing the chances that your page will be featured in enhanced search displays such as carousels, featured snippets, or knowledge panels.
Behind the scenes, schema markup uses a vocabulary hosted by Schema.org, a collaborative project founded by Google, Microsoft, Yahoo, and Yandex. This vocabulary includes hundreds of item types — such as Article, Product, Event, and FAQPage — each with its own set of properties that describe the content in detail. These properties give search engines more granular data to work with, improving content discoverability and interpretation. Schema in SEO is essential for helping bots make accurate associations between elements, rather than guessing their meaning from keywords alone.

To implement schema markup, you typically insert a block of JSON-LD code into the <head> or <body> of your HTML. Tools like Google's Structured Data Markup Helper, Schema.org’s generator, or AI platforms that automate markup can simplify the process for non-developers. Once added, it’s important to validate your schema using tools like Google's Rich Results Test or Schema Markup Validator to ensure everything is correct and eligible for enhanced search results. These tools help confirm that your structured data is properly formatted and optimized to meet Google's latest expectations.
Ultimately, schema markup doesn’t just enhance visibility — it enhances the precision with which your site communicates to search engines. This machine-readable layer of clarity is what powers many of today’s most advanced search features. When combined with traditional on-page SEO elements, schema gives your content the structural backbone it needs to compete for richer, more prominent search listings — making it one of the smartest upgrades in any beginner’s SEO strategy.
Key Types of Schema Markup Explained

Schema markup isn’t one-size-fits-all. It’s a broad framework with hundreds of schema types, each designed to describe a specific kind of content. Choosing the right type of schema — and applying it properly — can significantly improve your visibility in search results by helping Google match your content with the right search features. This is where understanding structured data SEO becomes critical: matching intent with schema type is what enables enhanced visibility.
One of the most commonly used types is Article schema. This is ideal for blogs, news updates, and educational content. It allows you to specify the author, headline, publishing date, article body, and even the associated images. When used correctly, Article schema increases the chance of your content appearing in Google’s Top Stories carousel or rich card displays. It’s especially useful for publishers or anyone producing frequent content updates, as it strengthens content authority in the eyes of search engines.
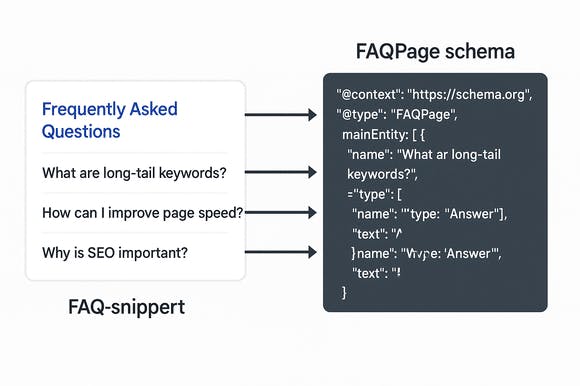
Another high-impact markup is FAQPage schema. This type allows you to structure a page that contains a list of frequently asked questions and their corresponding answers. When properly implemented, Google may display these directly in search results, making your site more clickable and informative at a glance. This format supports both user engagement and structured content delivery — a win for both UX and SEO. It’s also a powerful addition to knowledge base content or customer support hubs.
Product schema is essential for e-commerce websites. It highlights details like product name, brand, price, availability, ratings, and reviews — all of which are visible in search results as rich snippets. These enhancements don’t just attract attention; they can increase trust and drive more informed purchase behavior. For retailers or affiliate marketers focused on conversions, product schema in SEO is a critical differentiator in competitive markets.

Event schema enables websites to mark up information about upcoming events — including time, date, venue, performer, and ticket availability. This makes events discoverable through Google Search and Google Maps, especially for local audiences looking for nearby happenings. It also helps organize events by category and location, supporting both discoverability and calendar integration for users who want to save the date directly from search.
Other specialized schema types include LocalBusiness, Organization, Recipe, and Review — each offering structured visibility for highly specific content formats. LocalBusiness schema can list hours, location, and contact information; Recipe schema outlines ingredients, instructions, and nutrition; and Review schema helps feature testimonial-style content across service or product pages.
Understanding the differences between schema types is foundational for structured data SEO. Beginners don’t need to memorize every format, but they should learn to recognize when a certain schema type aligns with their content’s goal. Using Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper or an intelligent AI platform can take the guesswork out of schema selection — allowing even non-technical users to apply the right markup with confidence.
When your schema markup type matches the intent and format of your content, search engines can feature your page more accurately and prominently. That’s the power of schema in SEO: creating context where others offer only content.
Why Schema Helps Search Engines — and Why Google Cares

Search engines are designed to deliver the most accurate, useful, and relevant results for every user query. To do that, they must understand not just the words on a page but the context behind them. Schema markup enables that understanding by turning web content into structured, machine-readable data — allowing search engines to interpret it with precision. This makes schema an indispensable part of structured data SEO, especially for content creators aiming for top-tier placement in competitive search results.
Without schema, a search engine must rely on algorithms to infer the intent and organization of your content. But with schema, you're speaking the search engine's native language. You can explicitly declare that this block of text is an article, this number is a rating, this string is a product name, and this image is a logo. Schema removes the guesswork and replaces it with semantic accuracy — a critical factor in search engines' ability to deliver rich results.
Google in particular prioritizes schema because it strengthens the foundation of how content is indexed and displayed. Rich snippets, featured snippets, People Also Ask panels, knowledge graphs, and Google Discover cards are all fueled by structured data. Schema markup allows Google to extract key pieces of content and organize them visually, improving both the user experience and result relevance.

Structured data also streamlines the crawling and indexing process. Googlebot can more easily determine page purpose, scan relevant entities, and avoid duplication errors — all thanks to schema clarity. This efficiency improves crawl budget usage and enhances your site's overall SEO health, especially for larger or frequently updated websites.
Google has publicly emphasized its support for schema through tools, documentation, and Search Central updates. The Rich Results Test, Schema.org integration, and Google’s structured data guidelines are clear signals: using schema markup is no longer optional — it's a best practice. The reward for compliance is greater eligibility for visibility-enhancing features and a stronger presence across both desktop and mobile search.
As search evolves toward more conversational and context-driven queries — especially through voice search and AI assistants — schema becomes even more vital. It helps machines understand relationships, attributes, and actions within your content. This enables your pages to surface in intent-based scenarios, such as voice queries like "What are the best-rated SEO tools this year?" where schema-enhanced listings are preferred.
In summary, schema helps search engines because it provides structure where raw content can’t. Google cares because it leads to better results, happier users, and faster access to accurate information. And site owners should care because it directly influences how often — and how richly — their content appears in search.
Schema in SEO — Practical Use Cases & Beginner Mistakes
Schema in SEO isn’t just a technical add-on — it’s a practical tool that can influence how your content performs in real search environments. From blog articles to product pages, structured data helps bridge the gap between what your content says and how search engines understand it. When used effectively, schema can boost click-through rates, improve trust signals, and unlock eligibility for advanced SERP features like featured snippets and carousels.
One powerful use case is applying FAQPage schema to support content or service explanations. A standard list of frequently asked questions can be transformed into an interactive search result, where questions and answers appear directly in Google listings. This improves the user experience by surfacing relevant content faster — and it reinforces your authority as a helpful resource within your niche.
For product-based businesses, Product schema is especially valuable. Adding fields like name, brand, rating, review count, availability, and pricing provides rich context to search engines. When formatted correctly using structured data SEO, this markup results in star ratings, stock indicators, and pricing being shown directly in search results. This added visibility can boost click-through rates and improve conversion potential by giving users what they want up front.
 Publishers, bloggers, and content creators benefit from Article schema, which signals key information like the title, description, image, author, and publish date. This is particularly effective for getting content indexed rapidly and picked up by Google Discover or Top Stories, where structured context is a requirement for visibility.
Publishers, bloggers, and content creators benefit from Article schema, which signals key information like the title, description, image, author, and publish date. This is particularly effective for getting content indexed rapidly and picked up by Google Discover or Top Stories, where structured context is a requirement for visibility.
However, common beginner mistakes often dilute schema’s effectiveness. One of the most frequent is applying incorrect schema types. For instance, using Organization schema on a local landing page when LocalBusiness would be more appropriate, or using Review schema without tying it to a specific product or service.
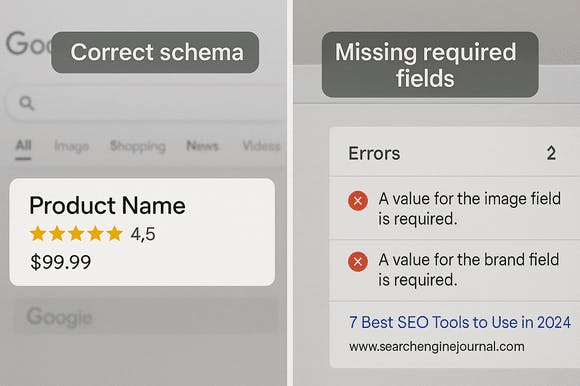
Another major issue is incomplete or invalid markup. Each schema type includes required and optional properties — skipping the essentials like a missing aggregateRating or product description can result in the markup being ignored entirely. Worse, it could generate a manual action or error warning in Google Search Console if it's misleading or incorrect.
Some users over-automate their schema strategy by relying entirely on plugins or themes that insert generic markup. While this may work in basic cases, it often lacks precision. Schema in SEO is most effective when it’s tailored to the page’s actual content and intent. Overuse or misuse — such as inserting five different schema types on a single page — can confuse crawlers and reduce your chances of getting rich results.
To avoid these issues, always use Google’s Rich Results Test or Schema Markup Validator to confirm your code is clean, complete, and valid. If you're using an AI tool to automate schema, make sure it generates markup based on the specific content and not just generic templates. Schema should clarify, not clutter — and when applied with precision, it becomes a strong ranking signal that supports visibility, relevance, and credibility in the eyes of both users and search engines.
How to Learn More or Start Using Schema

If you’re new to schema, the good news is that you don’t need to be a developer to get started. Thanks to a growing ecosystem of intuitive tools, automated platforms, and real-time validators, adding structured data to your site has never been more accessible. Whether you’re a content creator, local business owner, or SEO beginner, there’s a pathway that can match your skill level and goals.
One of the best entry points is Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper. This visual tool lets you highlight content on your website and assigns it to schema properties — then it outputs valid JSON-LD code you can insert into your site. It’s ideal for those who want to see how structured data SEO works without diving deep into manual coding. You can use it for marking up articles, products, events, and more.
For those who want a more foundational understanding, Schema.org is the authoritative source. It may look technical at first glance, but it provides exact definitions and requirements for each schema type. You’ll find examples of how to properly structure Product, FAQPage, Article, Review, and LocalBusiness markup. Learning to read schema documentation can help you spot plugin errors and build more precise structured data strategies.
Automation is another popular path. Platforms like WordPress offer plugins such as Rank Math, Yoast SEO, and SEOPress that automatically add schema to standard content types. While helpful, these tools aren’t foolproof — it’s important to check whether the markup they generate matches your actual page content. If you're serious about structured data SEO, treat automation as a starting point, not a replacement for validation.
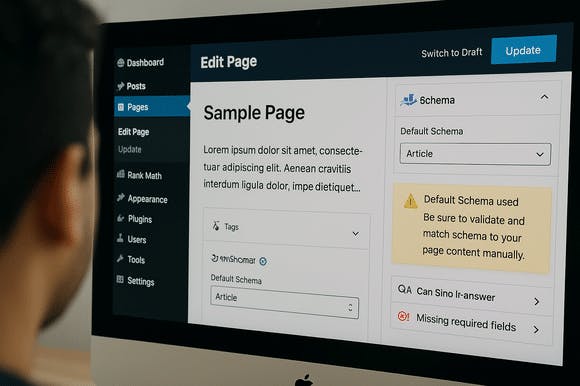
For AI-powered workflows, SEOBoostAI users can integrate schema markup directly into the article creation process. This ensures each page includes compliant Article, BreadcrumbList, and FAQPage schema, generated in context with the written content. When structured data is built alongside the content itself — rather than retrofitted later — it’s more accurate, relevant, and ready for indexing.
No matter what method you use, validation is non-negotiable. Tools like Google’s Rich Results Test and the Schema Markup Validator allow you to preview how your schema is interpreted by search engines. These tools flag missing fields, format errors, and eligibility issues that could prevent your markup from delivering rich results.
Once you’ve validated your implementation, continue learning by exploring schema relationships and more advanced types like HowTo, Course, JobPosting, or VideoObject. Each schema type has a specific purpose and benefit — and when applied properly, they create a detailed semantic map of your site that search engines can crawl, categorize, and reward with enhanced visibility.
Structured data SEO isn’t about adding code for the sake of it. It’s about improving how your content communicates with search engines. The best way to start is with one well-optimized page — then scale your schema strategy page by page, asset by asset, using the tools and guidance available. With time, your site won’t just rank better — it’ll be understood better.
Frequently Asked Questions

What is schema in SEO?
Schema in SEO refers to structured data markup added to your website’s code that helps search engines understand the meaning and context of your content. It enables enhanced search features like rich snippets, knowledge panels, and featured answers by translating on-page content into machine-readable data.
Do I need to know how to code to use schema?
No, you don’t need to be a developer to implement schema markup. Tools like Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper, SEO plugins such as Rank Math or Yoast, and platforms like SEOBoostAI allow you to add structured data without manual coding. Just make sure to validate your schema using Google’s Rich Results Test.
What types of content benefit the most from schema markup?
Schema markup is especially valuable for content like blog articles, products, reviews, FAQs, events, recipes, and local business listings. These content types often trigger enhanced display features in search results, which can improve visibility, click-through rates, and user trust.
Can using the wrong schema hurt my SEO?
Yes. Using the wrong schema type or omitting required properties can cause your markup to be ignored, trigger errors in Google Search Console, or in some cases, result in manual penalties for misleading structured data. Always match your schema to your content and validate it before publishing.
How does schema affect voice search and AI-powered results?
Schema helps search engines understand content relationships, context, and entities, which are essential for voice search and conversational queries. Structured data improves how content is retrieved and displayed in AI-driven experiences like Google Assistant, smart devices, and featured voice results.