Why Google Wants Schema

How Structured Data Helps Search Engines Deliver Better Results
Google's mission is simple: deliver the most relevant, useful information to users as quickly and accurately as possible. But in a sea of unstructured content, achieving that goal requires more than just crawling and indexing. It requires understanding — and that’s where schema markup comes in. Schema provides a clear, structured way for websites to communicate with Google, allowing it to interpret the meaning behind your content, not just the words on the page.
By embedding structured data into your webpages, you're essentially adding a layer of semantic clarity. This helps Google recognize the difference between a product review and a service listing, a recipe and an article, a person and a brand. That enhanced understanding powers features like rich snippets, carousels, knowledge panels, and other enhanced search experiences that can dramatically improve visibility and click-through rates.
For site owners focused on structured data SEO, this isn't just a technical upgrade — it's a strategic one. When Google can parse content more effectively, it rewards that clarity with richer search displays and better positioning. This is especially true in today’s AI-driven search landscape, where context and relevance are king. Implementing schema also aligns with Google's push toward more intuitive, answer-based search results across voice, mobile, and desktop environments.
If you're wondering what schema markup is or how it fits into a modern SEO strategy, this article will guide you through exactly what Google is looking for — and why structured data is one of the most important tools for sustainable search performance. From ranking signals to user experience enhancements, schema has become a foundational layer of SEO success.
What Schema Markup Actually Does

Schema markup plays a behind-the-scenes role that makes a significant difference in how your website appears and performs in search. While traditional HTML organizes content visually for users, schema markup organizes content semantically for search engines. It transforms basic content into structured, machine-readable data that tells Google what each element of your page truly represents — whether that’s an article, event, product, review, or service offering.
By applying schema, you help search engines interpret the purpose of your content with precision. Instead of seeing a string of text, Google can now understand that a number represents a product’s rating, that a date refers to an event, or that a paragraph contains a frequently asked question. This deeper understanding is exactly why Google structured data is such a high priority in search engine optimization today.
Schema markup also powers enhanced features in the search results, known as rich snippets. These may include star ratings, pricing details, recipe times, FAQs, or even availability indicators — all of which are pulled directly from structured data. When you implement schema correctly, you make your content eligible for these rich displays, which can dramatically increase visibility and click-through rates.

For those wondering what schema markup is and how it differs from standard SEO tactics, think of it as the connective tissue between your website and Google’s understanding. It doesn’t replace traditional ranking signals like backlinks or content quality — it enhances them by providing clarity. The more clearly Google can interpret your content, the more confidently it can surface your page in response to relevant queries.
This clarity is particularly important in competitive niches, where gaining even a slight edge in SERP presentation can result in more traffic and higher engagement. From a strategic standpoint, integrating structured data SEO into your optimization plan is about future-proofing your visibility — especially as voice search and AI-driven results increasingly rely on semantic data to determine relevance and context.
Why Google Prioritizes Structured Data

Google’s core objective is to deliver the most relevant, accurate, and useful information to users — instantly. To accomplish this, it needs to understand not just what content says, but what it *means*. That’s the role structured data plays in search. Unlike plain HTML, which provides layout and structure for humans, schema markup gives Google a semantic blueprint of your content. It defines relationships, identifies entities, and clarifies context — all of which enable Google to interpret your content more like a human would.
Structured data helps Google answer critical questions during the crawling and indexing process: Is this page about a person, a product, or a service? Is this a review, a tutorial, or an announcement? Without this clarity, Google must rely solely on keywords, headings, and links to infer meaning — and that guesswork often leads to less accurate search results. With schema, the uncertainty is removed. Google can confidently categorize and display your content in ways that align with the searcher’s intent.
This is exactly why Google structured data has become a central pillar of modern SEO strategy. Structured content powers a wide range of enhanced search experiences, including rich snippets, featured snippets, image carousels, and knowledge panels. These enhanced results don’t just look better — they perform better. Studies have consistently shown that pages using schema markup see higher click-through rates, greater SERP real estate, and improved engagement metrics.

Another critical factor is the role structured data plays in AI and voice search. As search queries become more conversational, Google increasingly depends on structured inputs to provide direct answers. Whether a user asks their phone “What’s the best Thai restaurant near me?” or “How do I install a ceiling fan?”, schema allows Google to extract relevant, trustworthy information and present it in featured results or spoken responses. In this AI-powered environment, structured data isn’t just helpful — it’s essential.
For site owners, this means implementing schema markup is more than a technical best practice. It’s a strategic alignment with how Google organizes and delivers information in 2025 and beyond. Whether you're optimizing a blog post, a product page, or a FAQ section, adding structured data helps ensure that your content is not only seen — but understood, indexed, and surfaced exactly when it’s needed most.
Real-World Examples of Schema in Action

The power of schema markup becomes crystal clear when you examine how it functions in real-world search results. Structured data doesn’t just sit silently in your website code — it directly influences how your content is displayed, interpreted, and interacted with in Google’s search engine results pages (SERPs). These enhancements are known as rich snippets, and they often represent the difference between a basic text listing and a highly visible, high-engagement result.
Take the example of a recipe blog. Without structured data, Google sees the page as just another article. But with schema markup applied — specifically the “Recipe” type — Google can extract details like cook time, ingredients, calorie count, and user reviews. This transforms your listing into an eye-catching search result that includes a photo, star rating, and quick-reference information, increasing both its relevance and its appeal. For food bloggers and publishers, this kind of enhanced appearance can significantly boost traffic and time on site.
Another powerful use case involves FAQ schema. When applied to content that answers common questions, this schema allows Google to display those answers directly under your link in the search results. It’s a practical way to gain additional SERP space and demonstrate authority, especially when targeting question-based or voice search queries. In industries like health, finance, and service-based businesses, this format helps establish trust and increases the likelihood of clicks — all while improving the user experience.

E-commerce websites benefit heavily from Product schema. By marking up details such as price, availability, brand, and user reviews, businesses make their listings eligible for rich product results. These can include star ratings, “in stock” tags, and pricing information that users can see at a glance. This level of detail not only improves visibility but also increases conversion rates, since users are more informed before clicking through. In competitive niches, structured data is often what separates high-performing listings from those that go unnoticed.
Local business schema is another common implementation. It helps Google understand physical location, hours of operation, services offered, and customer ratings. For small businesses trying to rank in local packs or voice searches (like “coffee shop near me”), having accurate, structured data is critical. Without it, Google may ignore or misinterpret the business entirely, even if the page ranks organically.
Across all these examples, the underlying advantage is clear: schema markup helps Google understand, categorize, and display your content in ways that drive more engagement. Whether you're focused on structured data SEO for blog posts, product listings, service pages, or educational content, implementing the right type of schema makes your content easier to surface in high-intent searches. That’s the true value of structured data — it transforms content from visible to discoverable, and from indexed to prioritized.
How Schema Improves Visibility and Engagement

The true strength of schema markup lies in its ability to enhance how your content is presented and perceived in search results. Unlike standard listings that rely solely on meta titles and descriptions, schema-enriched content can trigger rich snippets — enhanced search previews that include images, ratings, FAQs, pricing, and more. These visual and informational enhancements don’t just make your listing look better — they make it more useful, more trustworthy, and far more clickable.
In an increasingly crowded search landscape, earning attention is half the battle. By implementing structured data, you’re giving your content a way to visually stand out from competitors who may rank similarly but lack schema integration. For example, if two websites are ranking for “best espresso machine,” and only one displays product ratings, pricing, and availability in the search preview, users are far more likely to click the enriched result. That difference can translate into significant gains in traffic and user engagement.
But schema does more than enhance appearance — it improves how Google interprets and connects your content to user intent. Structured data provides a semantic framework that helps the search engine determine which queries your content best answers. This is particularly important in AI-driven and voice search environments, where conversational queries require high levels of contextual understanding. A query like “What’s the average lifespan of a French bulldog?” is more likely to trigger a snippet from a page with properly structured FAQ or Article schema than one with plain text alone.

Schema also plays a vital role in mobile and zero-click search behavior. On mobile, where screen space is limited, rich results dominate visual hierarchy. A page with structured data is more likely to be featured in top-position elements like carousels, featured snippets, or “People also ask” sections. These placements can lead to increased visibility even when users don’t click — and when they do, it's with clearer intent and higher conversion potential.
From a user experience standpoint, schema improves alignment between the search preview and the content that follows. When users click on a listing expecting a recipe, tutorial, or product review — and your structured data has prepared them accurately — they’re more likely to stay, read, and engage. This reduced bounce rate and increased dwell time are behavioral signals that further reinforce your site’s authority in Google’s algorithm.
Ultimately, structured data SEO isn’t just about technical markup — it’s about improving the dialogue between your content and both search engines and users. When you implement schema correctly, you give your site the tools to speak Google’s language, stand out visually, and connect with searchers more effectively — all of which contribute to long-term SEO success.
Avoiding Common Mistakes with Schema Implementation

Schema markup offers undeniable SEO advantages — but only when it’s implemented correctly. For many beginners, structured data can feel intimidating, leading to errors that prevent Google from recognizing or rewarding the markup. Understanding the most common mistakes will help you avoid wasted effort and ensure your schema contributes meaningfully to your structured data SEO strategy.
One of the most frequent issues is choosing the wrong schema type. For instance, marking up a tutorial as an “Article” instead of a “HowTo” limits its eligibility for step-by-step rich features. Similarly, labeling a product review as a generic “WebPage” misses out on enhanced elements like star ratings and pricing. Google’s structured data system rewards precision — the closer your markup matches the content’s actual purpose, the more likely it is to be featured prominently in SERPs.
Another major error is using improperly formatted or invalid JSON-LD. Google prefers JSON-LD for schema markup, but even a minor syntax error — like a missing bracket, comma, or quotation mark — can break the entire markup block. This often goes unnoticed until a page fails to qualify for rich snippets. To avoid this, every piece of structured data should be tested using tools like the Google Rich Results Test and the Schema Markup Validator.
Many site owners also rely too heavily on plugins or automated schema tools. While these can be helpful, they often apply overly generic markup or fail to update dynamically as content evolves. For example, a plugin may label every blog post as a standard “Article,” even when a page is better suited for “FAQPage,” “Review,” or “Product” schema. Without manual refinement, this approach results in missed opportunities and misleading signals to Google.

Another common mistake is omitting required fields. Google won’t display rich results if your schema is incomplete — even if the structure itself is valid. For example, if you use “Product” markup but leave out the price or availability, the listing won’t be eligible for product-specific enhancements. Always refer to Google’s structured data documentation to ensure every required and recommended property is included.
Stale or outdated schema is another issue that goes overlooked. If you update your webpage content but don’t update the corresponding schema, Google may see mismatched information, which can undermine trust and cause your markup to be ignored. Just like meta titles and descriptions, schema needs to evolve as your content does — especially for events, local business listings, and product pages with changing inventory or prices.
Finally, some users add multiple conflicting schema types to a single page, confusing Google’s interpretation of the content. For example, combining “Review,” “Product,” and “FAQPage” markup improperly can dilute the signal or make the page ineligible for all of them. Schema should be used intentionally — tailored to the primary content focus of the page.
Correctly implemented schema markup sends strong signals to Google about what your content represents. But when it’s incomplete, misapplied, or invalid, it creates noise rather than clarity. By avoiding these common missteps and validating your structured data regularly, you not only protect your eligibility for rich results — you strengthen your entire SEO foundation.
Does Schema Help Rankings? What the Data Shows
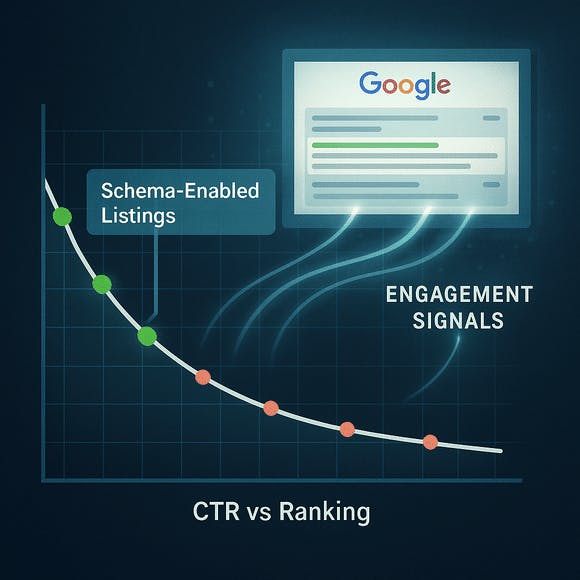
One of the most frequently asked questions about schema markup is whether it has a direct impact on search engine rankings. According to Google’s official position, structured data is not a direct ranking factor — meaning its presence alone won’t push your page higher in the search results. However, that doesn’t tell the whole story. In practice, schema plays a critical indirect role in SEO performance, and the data shows that its effects are both measurable and meaningful.
The most obvious benefit of schema is its ability to enhance search result listings through rich snippets. These enriched previews — including star ratings, pricing, availability, review counts, FAQs, and images — make your content more visually compelling. Users are drawn to listings that provide more value at a glance, and that increased attention leads to higher click-through rates (CTR). Numerous case studies have shown that implementing structured data can increase CTR by 20% or more, even when the page’s ranking remains unchanged.
Higher engagement doesn’t just improve traffic — it sends important behavioral signals to Google. When users consistently click on a page and stay to consume the content, that page is seen as more relevant and valuable. Over time, these signals can contribute to improved rankings. So while schema doesn’t directly change your ranking position, it can influence the metrics that Google uses to evaluate content performance.
Structured data also improves how Google indexes your content. With schema, your site sends clearer signals about the context and intent of your pages. This semantic clarity helps search engines determine whether your page is the best match for a given query — especially for featured snippets, AI-generated summaries, and voice search results. In a search environment increasingly driven by natural language and intent, this context is more important than ever.
Additionally, structured data SEO supports long-term authority building. When your content consistently appears in enhanced formats — such as knowledge panels, product displays, or FAQ expansions — it increases your brand’s visibility and credibility. Users begin to associate your site with trust, expertise, and relevance. These psychological signals can translate into backlinks, repeat visits, and social sharing, all of which indirectly contribute to stronger rankings.
So, does schema markup directly boost rankings? No — but it sets the stage for everything that does. It improves how your content is displayed, how it’s understood by Google, and how it engages with users. In an SEO strategy built for modern search, structured data isn’t optional. It’s a critical support system that helps all your other efforts perform better, faster, and more reliably.
How to Start Using Schema on Your Site

Adding schema markup to your website doesn’t require advanced technical skills — in fact, there are multiple beginner-friendly ways to get started, even if you’ve never worked with code. The key is to focus on accuracy, simplicity, and alignment with your content type. Once you understand the basics, implementing structured data becomes a straightforward process that delivers long-term SEO value.
The most recommended method is using JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data), which is Google’s preferred format for schema markup. JSON-LD is placed within the <head> section of your page and doesn’t interfere with your visible content. If you’re comfortable editing HTML, you can manually copy, customize, and paste schema blocks using templates from Schema.org. Each schema type — such as Article, FAQPage, Product, or LocalBusiness — comes with examples that show you exactly which fields are required.
For those using platforms like WordPress, Shopify, or Wix, many SEO plugins and themes include built-in schema features. Tools like Rank Math, Yoast SEO, and Schema Pro allow you to apply schema types with just a few clicks. However, it’s important to review and customize these settings, as plugins often default to generic markup that may not fully match your content.
Google also offers free tools to help with implementation. The Rich Results Test allows you to check if your structured data is eligible for enhanced SERP features, while the Schema Markup Validator identifies errors or missing fields. Both tools are essential for confirming that your markup is correctly formatted and fully supported by Google.

If you’re unsure where to start, begin with the most impactful and widely supported schema types:
- WebPage: Establishes the identity and context of the page and can wrap other schemas
- BreadcrumbList: Displays breadcrumb navigation in the SERP and improves internal hierarchy clarity
- Article: For blog posts, news, and educational content
- FAQPage: For question-and-answer formats
- Product: For e-commerce or service listings
- LocalBusiness: For businesses with a physical location
- Review: For content that evaluates products or services
When adding schema, always use real data from the page itself — never insert misleading or unrelated information just to trigger rich results. Google’s guidelines are strict, and violations can result in manual penalties or markup being ignored. Focus on consistency between your structured data and on-page content.
Whether you're using a plugin or adding markup manually, structured data SEO is a skill that improves with practice. Start with one content type, validate your markup, and monitor results. As you become more confident, you can expand your use of schema across other pages — building a stronger foundation for long-term search visibility and engagement.
Conclusion & Final Takeaways

In today’s search environment, standing out isn’t just about having great content — it’s about making that content understandable, indexable, and aligned with user intent. That’s where schema markup comes in. Structured data has become a foundational layer of SEO, not because it directly manipulates rankings, but because it empowers Google to interpret and display your content with far greater accuracy and impact.
Throughout this article, we’ve explored how schema serves multiple strategic roles. It enhances your search listings through rich snippets, improves click-through rates by providing users with more context at a glance, and strengthens Google’s ability to understand what your page is truly about. It also plays a critical supporting role in AI-powered and voice-based search environments, where clarity and structure are essential for surfacing accurate results.
For beginners, one of the most important takeaways is that schema doesn’t have to be overwhelming. You don’t need to implement every schema type across every page to start seeing results. A single FAQPage markup, a properly tagged product listing, or a well-structured blog post can open the door to better visibility and user engagement. Over time, as your comfort grows, you can expand your use of structured data strategically across your entire site.
Structured data also positions your site for the future. As Google continues to shift toward more semantic, conversational search experiences — particularly in voice and AI-driven formats — having clear, structured signals will be a key factor in remaining competitive. Schema helps you communicate your content’s intent and meaning directly to Google, reducing ambiguity and increasing your eligibility for high-impact placements like featured snippets and knowledge panels.
It’s worth emphasizing that structured data SEO is not just for large companies or advanced developers. With today’s tools, templates, and plugin ecosystems, any site owner can implement schema — and those who do gain a powerful edge in search. It’s not about chasing algorithms; it’s about delivering clarity, value, and relevance in the format Google is actively encouraging.
In the end, schema is about more than code. It’s about creating a stronger connection between your content and the people searching for it. When you use schema markup correctly, you’re not just optimizing for search engines — you’re optimizing for the user experience, trust, and long-term discoverability. And that’s what great SEO is all about.
Frequently Asked Questions

What is schema markup and why does Google use it?
Schema markup is a type of structured data that helps Google understand the meaning behind the content on your website. It allows search engines to interpret your pages more accurately and enables features like rich snippets, knowledge panels, and voice search responses.
Does schema markup improve my rankings in Google?
Schema markup is not a direct ranking factor, but it improves visibility by enabling rich search features. These enhancements increase click-through rates and user engagement, which can lead to better long-term SEO performance.
What types of schema should beginners start with?
Beginners should focus on widely supported schema types like WebPage, Article, FAQPage, Product, and BreadcrumbList. These formats are simple to implement and offer clear SEO and user experience benefits.
How do I test if my schema markup is working?
You can use Google’s free tools — the Rich Results Test and Schema Markup Validator — to confirm that your structured data is valid and eligible for enhanced search features. These tools highlight errors and show what Google detects from your markup.
Can I use schema on all pages of my website?
Yes, but it’s important to use the correct schema type for each page. Applying irrelevant or incorrect schema can lead to penalties or markup being ignored. Always match the schema to the actual content and update it as your site evolves.